HTML Elements
HTML Elements
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag:
The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
| Start tag | Element content | End tag |
|---|---|---|
| <h1> | My First Heading | </h1> |
| <p> | My first paragraph. | </p> |
| <br> | none | none |
Nested HTML Elements
HTML elements can be nested (this means that elements can contain other elements).
All HTML documents consist of nested HTML elements.
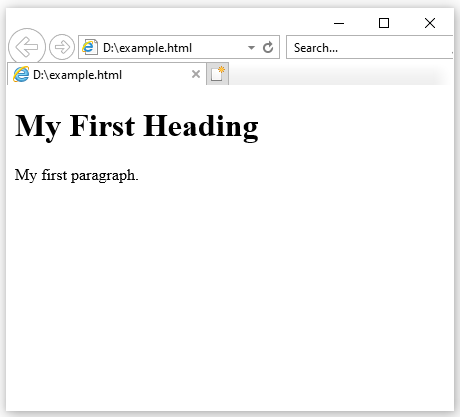
The following example contains four HTML elements (<html>, <body>, <h1> and <p>):
Example
<html>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output :
Example Explained
The <html> element is the root element and it defines the whole HTML document.
It has a start tag <html> and an end tag </html>.
Then, inside the <html> element there is a <body> element:
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
The <body> element defines the document's body.
It has a start tag <body> and an end tag </body>.
Then, inside the <body> element there is two other elements: <h1> and <p>:
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
The <h1> element defines a heading.
It has a start tag <h1> and an end tag </h1>:
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
The <p> element defines a paragraph.
It has a start tag <p> and an end tag </p>:
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
Never Skip the End Tag
Some HTML elements will display correctly, even if you forget the end tag:
Example
Empty HTML Elements
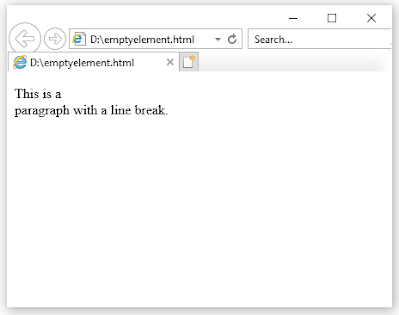
HTML elements with no content are called empty elements.
The <br> tag defines a line break, and is an empty element without a closing tag:


Comments
Post a Comment